ETHFI Coin

What Is ETHFI Token?
ETHFI is the governance token of the Ether.fi protocol, enabling holders to vote on protocol parameters, fund allocations, and ecosystem development proposals. Ether.fi operates as a staking and restaking platform built on Ethereum. When users deposit ETH, they receive eETH—a liquid staking token that represents both their staked assets and the ability to earn rewards while using the token across other DeFi applications. The protocol leverages EigenLayer to restake these assets, providing security to external networks and generating additional yield.
Within this system, eETH functions as a "receipt" for usable funds, while ETHFI serves as the "vehicle of governance." Their roles differ: eETH focuses on capital utility and yield, while ETHFI centers on voting and governance.
ETHFI Token (ETHFI): Current Price, Market Cap, and Circulating Supply
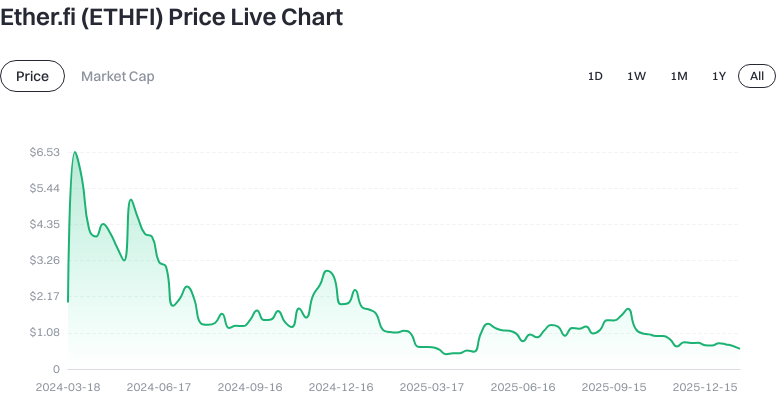
As of 2026-01-22 (data source: market snapshot):
- Latest price: approximately $0.602500.
- Circulating supply: about 699,462,910 tokens; total and max supply: 1,000,000,000 tokens.
- Circulating market cap: around $602,500,000; fully diluted market cap: about $602,500,000.
- Price change: -0.35% (1hr), -1.99% (24hr), -21.22% (7d), -14.84% (30d).
- 24-hour trading volume: approximately $862,218.57; market dominance: 0.018%.
Explanations:
- Circulating supply refers to the number of tokens available for trading on the market.
- Fully diluted market cap is calculated as “current price × max supply” and estimates the potential valuation if all tokens are released.
- Trading volume represents the fiat value of transactions in the past 24 hours, reflecting liquidity activity.
ETHFI’s price and volatility are influenced by market sentiment and token unlock schedules. Always assess real-time quotes with candlestick charts and order book depth to evaluate liquidity before trading.
Who Created ETHFI Token (ETHFI), and When?
ETHFI was launched by the Ether.fi team on 2024-03-17 as the protocol’s governance token for community voting and protocol decision-making. Ether.fi is designed as a staking and restaking platform on Ethereum, with eETH as its core product for DeFi utility. As EigenLayer’s restaking ecosystem expands, Ether.fi increasingly allocates staked assets to secure external services—broadening revenue streams and collaborative opportunities.
Early token distributions typically target ecosystem participants and community members. Governance aims to increase transparency and sustainability in key protocol parameters and incentive mechanisms; distribution details follow official announcements.
How Does ETHFI Token (ETHFI) Work?
There are two main functional lines:
-
Capital Flow: Users stake ETH with Ether.fi to receive eETH. Staking involves locking tokens to support network consensus and earn block rewards. The protocol then leverages EigenLayer for restaking—reusing these economic guarantees to secure external services (such as layer 2 sequencing or oracles) in exchange for additional service rewards.
-
Governance: ETHFI is a governance token that allows holders to vote or propose changes regarding protocol parameters, incentive structures, treasury allocation, etc. Governance tokens grant rights related to protocol management but do not represent equity or direct claims to revenue—specific powers are defined in the governance charter.
Key Terminology:
- Restaking: Using staked assets’ economic security to underwrite additional networks or services without withdrawing the underlying assets, earning incremental yield.
- EigenLayer: An Ethereum-based restaking infrastructure connecting stakers to external services (referred to as AVS—Actively Validated Services).
- AVS: Actively validated services, such as rollup sequencers (for L2 scaling solutions), security councils, or oracles that securely bring off-chain data on-chain.
What Can You Do With ETHFI Token (ETHFI)?
For holders:
- Governance voting and proposals: Participate in decisions on protocol fees, incentive distributions, risk parameters, and more.
- Ecosystem participation credential: Some community initiatives, tests, or incentives may consider governance activity or token holdings—refer to official guidelines.
For eETH holders:
- eETH is designed for capital utility: Use it as collateral in DeFi lending, trading, or liquidity provision to maximize capital efficiency. For example, you can borrow stablecoins against eETH for short-term needs or provide liquidity to earn fees and rewards (assess risks vs. returns independently).
Wallets and Integrations in the ETHFI (ETHFI) Ecosystem
- Wallet options: Mainstream non-custodial wallets supporting Ethereum mainnet—such as browser extensions and hardware wallets—can manage both ETHFI and eETH. Non-custodial wallets mean users control their private keys and seed phrases.
- Hardware wallets: Secure private keys offline in physical devices, reducing malware risk—ideal for long-term storage or large holdings.
- Network and asset verification: When withdrawing or bridging tokens, always verify the network (typically Ethereum mainnet) and contract addresses from official documentation or websites to avoid phishing risks.
- Extensions and integrations: As restaking expands, eETH can be used across more applications; governance tools (such as voting interfaces) typically provide signature and proposal modules—follow official channels for updates.
Main Risks and Regulatory Considerations for ETHFI Token (ETHFI)
- Market volatility: Price is subject to broader crypto trends and token unlock schedules; short-term volatility can be significant.
- Smart contract & restaking risks: Underlying contracts, cross-component integrations, and AVS operations may face technical or economic model vulnerabilities—including slashing misfires or service outages.
- Liquidity risk: During certain periods, low trading depth can increase slippage and price volatility.
- Governance concentration: If voting power is held by a few addresses, proposal diversity and robustness could be impacted.
- Regulatory uncertainty: Jurisdictions differ in their treatment of token attributes and restaking services; always comply with your local regulations.
- Account security: Both exchange accounts and non-custodial wallets should enable security measures such as 2FA, hardware signing, and offline backup of seed phrases.
How to Buy and Safely Store ETHFI Token (ETHFI) on Gate
Step 1: Register and log in at Gate (gate.com), complete identity verification (KYC), and enable two-factor authentication (2FA) for enhanced account security.
Step 2: Deposit or purchase USDT. You can transfer funds via blockchain or fiat channels—always ensure network/address match; test with a small amount before transferring larger sums.
Step 3: Search for “ETHFI/USDT” on the trading page. Choose your order type: limit orders let you set custom buy prices; market orders fill instantly at current prices. Review price, quantity, and fees before confirming.
Step 4: After purchase, manage your assets. For short-term trading, you may leave funds on the exchange with risk controls; for mid-to-long-term holding, withdraw to a non-custodial wallet. Select the correct network (usually Ethereum mainnet), verify the token contract address, and test with a small transfer first.
Step 5: Secure storage. Use a hardware wallet or reputable non-custodial wallet; back up seed phrases/private keys offline—never store screenshots or save them in the cloud. Regularly review wallet approvals and revoke unnecessary permissions to prevent unauthorized asset use.
ETHFI Token (ETHFI) vs. LidoDAO
Both protocols issue governance tokens but serve different roles. Ether.fi is natively focused on “restaking,” using EigenLayer to allocate staked assets for securing external services; LidoDAO centers on “liquid staking,” where its main token is LDO and its liquid staking receipt is stETH.
- Positioning & Yield: eETH tied to ETHFI can generate returns from Ethereum staking rewards plus restaking incentives; Lido’s stETH mainly mirrors Ethereum staking rewards. Restaking offers potential extra yield but introduces additional risks from external services.
- Risk exposure: The ETHFI ecosystem has deeper integration with AVS/restaking paths—requiring attention to layered protocol risk; Lido focuses mainly on validator operations and staking security.
- Governance scope: ETHFI governance is about Ether.fi’s parameters/ecosystem initiatives; LDO governs Lido’s protocol settings and validator management. Neither token represents equity—governance rights are set by their respective charters.
Summary of ETHFI Token (ETHFI)
ETHFI is a governance token at the center of Ethereum’s staking/restaking ecosystem, working alongside eETH to create dual tracks for “capital utility” and “governance.” As of the 2026-01-22 snapshot, both circulating market cap and price are dynamically changing with notable short-term volatility. For users interested in Ethereum’s ecosystem and compounded restaking yields, it’s crucial to understand how Ether.fi operates—alongside EigenLayer’s mechanisms and AVS-related risks. Best practice is to start with small deposits to familiarize yourself with staking/restaking flows; fund your Gate account stepwise for trading. Long-term holders should prioritize non-custodial storage with diligent backups, track governance proposals/audits regularly, allocate within risk tolerance, and periodically review positions.
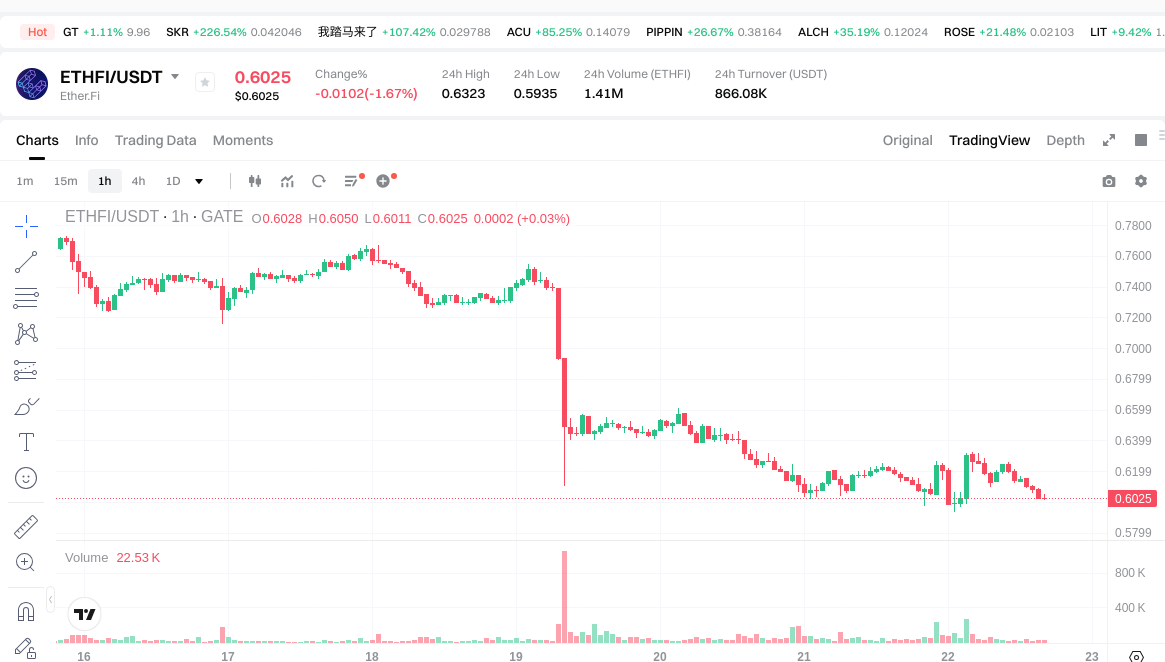
See ETHFI USDT price
FAQ
What Is ETHFI Mainly Used For?
ETHFI is a governance token within the Ethereum ecosystem that enables holders to participate in decision-making votes on the Ether.fi protocol. It incentivizes users to engage in Ethereum staking and liquid staking—earning staking rewards while holding governance power. Through ETHFI, community members vote on protocol direction, fee structures, and new feature proposals.
How Can I Earn Staking Rewards with ETHFI?
By staking ETHFI tokens you can earn a share of fees generated by the protocol. Purchase ETHFI on major exchanges such as Gate, then deposit into a supported staking wallet or protocol. Note that staking usually involves lock-up periods; early withdrawals may incur penalties—review terms carefully before participating.
How Is ETHFI Token Related to Ethereum’s ETH?
ETHFI is an independent governance token based on Ethereum; ETH is Ethereum’s native asset. Ether.fi operates as a liquid staking protocol within the Ethereum ecosystem—ETHFI governs the protocol itself. The two complement each other but serve different functions; holding ETHFI does not equal holding ETH—but using Ether.fi services generally requires interacting with ETH.
How Can Beginners Safely Buy and Store ETHFI?
Buy ETHFI with stablecoins like USDT on reputable exchanges such as Gate. For better security, transfer your ETHFI holdings into a non-custodial wallet (like MetaMask) rather than leaving them long-term on an exchange. Before using a non-custodial wallet, securely record your private key/seed phrase—never share them with anyone or any platform.
Is ETHFI Price Volatile? What Risks Should Be Noted?
As a governance token, ETHFI price tends to be volatile—sensitive to market sentiment and regulatory developments. Main risks include insufficient liquidity leading to slippage risk, smart contract vulnerabilities, and lock-up risks during staking periods. Always research project fundamentals thoroughly before investing—only allocate capital you can afford to lose.
Quick Glossary for ETHFI Token (ETHFI)
- Ethereum ecosystem: The collection of applications, protocols, and assets built on the Ethereum blockchain.
- Liquid staking: Users stake assets for yield while receiving liquid receipt tokens usable in DeFi activities.
- Smart contract: Self-executing code deployed on a blockchain that facilitates transactions without intermediaries.
- Gas fees: Computational costs paid for executing transactions/contracts on Ethereum.
- Token staking: Locking tokens in a protocol for rewards or governance participation.
- DeFi protocols: Decentralized financial protocols offering lending, trading, derivatives, etc.
Further Reading & References for ETHFI Coin (ETHFI)
-
Official Website / Whitepaper:
-
Development / Documentation:
-
Authoritative Media / Research:
Related Articles

In-depth Explanation of Yala: Building a Modular DeFi Yield Aggregator with $YU Stablecoin as a Medium

Sui: How are users leveraging its speed, security, & scalability?
